Program LAKTO - byl zrušen a nyní ho nelze objednat.
Můžete si vybrat z aktuální nabídky programů, děkujeme za pochopení
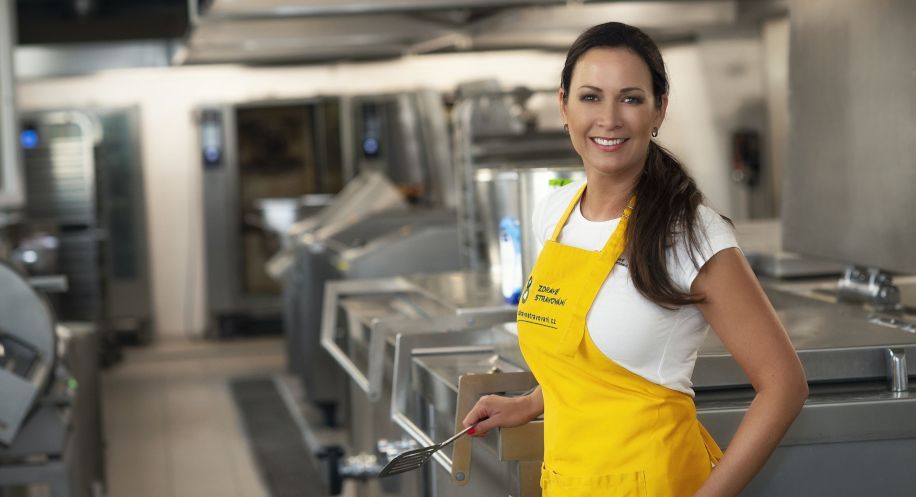
AKTUÁLNÍ NABÍDKA PROGRAMŮ
More details about the LACTO- programme:
- dietary meal plan for lactose intolerance
- varied and balanced diet
- Special lactose-reduced dairy products or alternative raw materials are included
- ideal for those regulating the lactose content of their diet
- not suitable for milk protein allergy
- only available in a three-course meal combination (breakfast+lunch+dinner), no exceptions or substitutes permitted
- the selected daily energy value of the programme is divided into 3 courses
 Ingredients
Ingredients
The dairy products used in the Lacto programme are lactose-reduced.
 Nutrition window
Nutrition window
Lactose intolerance affects approximately 10-20% of the Czech population, and most of them develop it secondary to diseases of the small intestine mucosa, which may be related to Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, etc.
With advancing age, the amount and activity of an enzyme called lactase can physiologically decrease in humans, causing the typical difficulties associated with lactose intolerance or lactose absorption. If the enzyme is ineffective or reduces its activity completely, lactose is no longer broken down as we need it to be. Instead, it moves to the large intestine, where it is fermented by micro-organisms and starts to cause typical bothersome digestive problems. In these cases, low-lactose or lactose-free products offer a workable solution. This principle is precisely applied in the boxed diet Lacto- program. Few people know that the lactose content drops by 20-30% during fermentation, so cottage cheese, yoghurt, kefir, and acidophilus milk, for example, may not be a problem for people with intolerance. In cheese production, most of the lactose is transferred to the whey, so the lactose content of hard cheeses is almost zero.
Cow’s milk protein allergy is more severe and works by a completely different mechanism than lactose intolerance. People with a proven cow’s milk protein allergy must follow a strictly dairy-free diet. This consists in the absolute exclusion of dairy products containing not only cow’s milk, but also goat’s or sheep’s milk. These milks have similar allergenicity. An allergy to cow’s milk protein (ABKM) causes an overreaction of the immune system. The reaction is mainly caused by abdominal pain, diarrhoea, often with blood in the stool, but it can also manifest itself as urticaria or eczema. ABKM is one of the most common food allergies in children under 3 years of age, while it is rather rare in adults. It is caused by products containing milk protein. Dairy is replaced by vegetable drinks made from soya, nuts, rice, or oats on a dairy-free diet.

Seitan s omáčkou Teriyaki, basmati rýže

Kuřecí s anglickou slaninou, cibulí a paprikou, pečené brambory

Špaldové pukance a višňový tvaroh

Směs listových salátů s tuňákem

Hovězí na víně, žampiony, šťouchané brambory

Kančí se šípkovou omáčkou s rakytníkem, muffin z quinoa a rýže

Dip z pečené dýně, knuspi, borůvky

















 Ingredients
Ingredients Nutrition window
Nutrition window









 Dessert
Dessert Fresh
Fresh


